As an OEM, you're under pressure to control costs. You see a steel rim as a simple component and choose a supplier based on the lowest price, but then reports of cracked welds and bent flanges start coming in from the field.
Technical expertise is crucial because agricultural rims are not commodities; they are engineered components. A knowledgeable supplier ensures the correct high-strength steel1, precision manufacturing processes2, and rigorous testing are used, directly impacting the tractor's durability, safety, and brand reputation.

I remember talking to an engineering lead at a major tractor manufacturer. They had switched to a low-cost rim supplier to save a few dollars per unit. Six months later, they were facing a multi-million dollar warranty crisis. Their new, powerful tractors were literally cracking their own wheels in the field. The problem wasn't the tractor's design; it was the rim's material and poor-quality welds that couldn't handle the specified torque and load. They learned the hard way that a steel rim isn't just a ring of metal; it's a critical safety component that requires deep technical understanding.
How Does Material Science Impact a Rim's Durability?
You receive two steel rims that look identical, but one is 20% cheaper. It's tempting to think steel is just steel, but this assumption can lead to catastrophic field failures and damage your brand's reputation.
The specific steel alloy determines the rim's ability to handle high loads and resist metal fatigue3. High-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels provide superior durability and load-bearing capacity compared to standard carbon steel, preventing cracks and deformation under constant stress.
The choice of raw material is the foundation of a reliable rim. For modern, high-horsepower tractors, standard steel is not enough. We insist on using high-strength alloys because they contain small amounts of other elements, like manganese and carbon, which dramatically increase their strength without adding unnecessary weight. This is critical. A rim must endure the constant cyclical stress of plowing, hauling, and operating on uneven terrain. This repetitive loading causes metal fatigue3, which is the primary cause of cracks around the bolt holes or weld joints. A rim made from an inferior alloy will fail from fatigue much sooner, no matter how well it is manufactured. A technically proficient supplier doesn't just sell you a rim; they verify the material science behind it to guarantee it can survive in the real world.
Standard Steel vs. High-Strength Alloy
| Feature | Standard Carbon Steel | High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Strength-to-Weight Ratio | Lower | Higher |
| Fatigue Resistance | Standard | Significantly Increased |
| Impact Durability | Prone to deformation | Resists impacts and cracking |
| Ideal Application | Light-duty, low-stress | High-load, high-torque tractors |
Why Does Manufacturing Precision Matter More Than Raw Materials?
You specified the correct high-strength steel1, yet your rims are still failing at the weld seams4 or bending out of shape. The best materials in the world can be rendered useless by a poor manufacturing process.
Manufacturing precision—specifically in forming, welding, and finishing—is critical because it preserves the integrity of the steel. Improper techniques create weak points and stress concentrations that lead to premature failure, regardless of the material's quality.
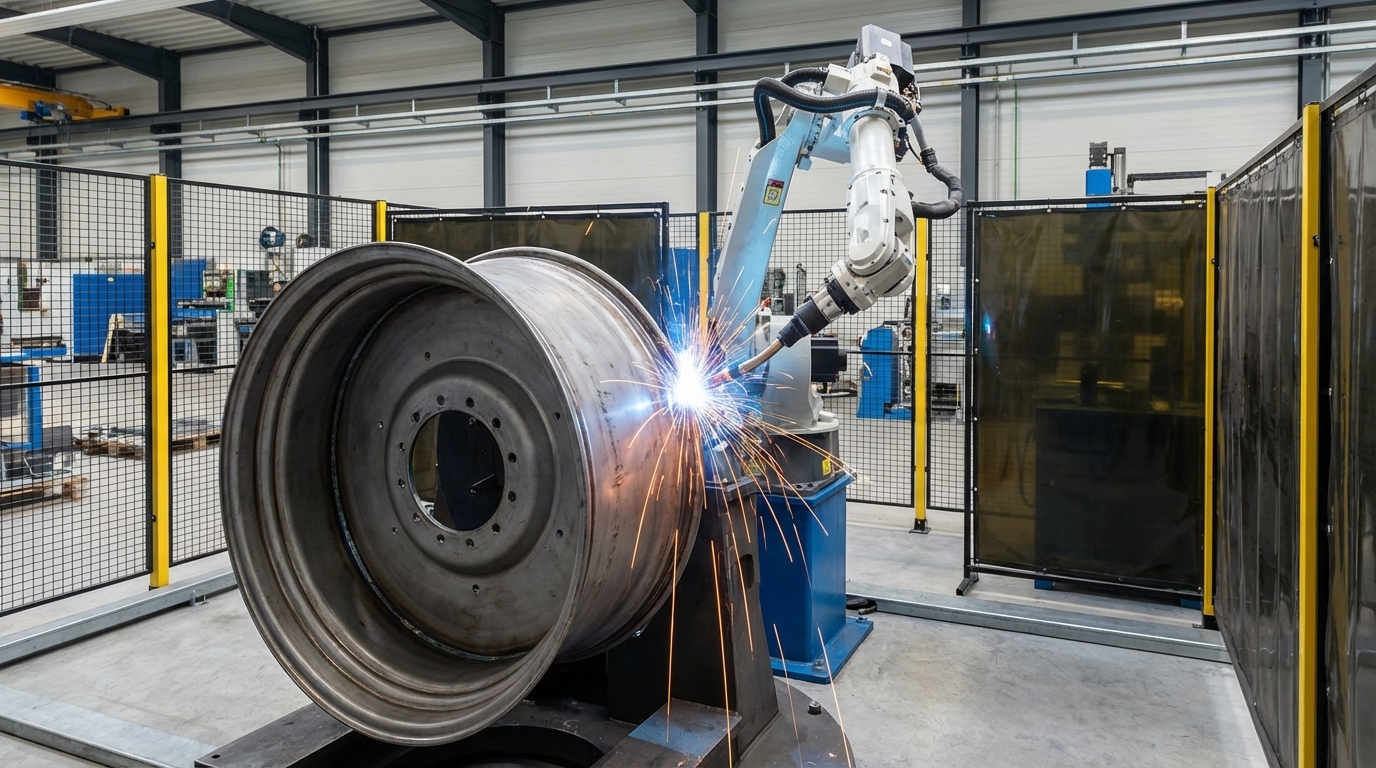

A perfect piece of high-strength steel1 is only as good as the processes used to shape it. I've seen firsthand how cutting corners here creates disaster. For example, during the forming process, if the rim disc isn't perfectly round or the gutter isn't shaped with uniform pressure, it creates hidden stress points. Later, under load, a crack will start right there. The welding is even more critical. An improper weld doesn't fully penetrate the metal, creating a superficial bond that looks fine but will snap under the immense torque of a tractor. We use advanced, automated welding5 to ensure every seam is flawless and as strong as the parent metal. Finally, the finishing process, from deburring sharp edges to applying a durable coating, prevents corrosion, which can weaken the steel over time. A supplier without this technical focus is just assembling metal; a true partner is engineering a component.
Critical Manufacturing Stages
- Precision Forming: Ensures the rim is perfectly concentric and free of stress risers, which prevents wobbling and fatigue.
- Automated Welding: Guarantees deep, consistent penetration for welds that are as strong as the steel itself.
- Protective Finishing: A high-quality paint or powder coat prevents rust and corrosion, which can compromise the rim's structural integrity.
How Do Rigorous Testing Protocols Ensure Field Reliability?
A rim looks perfect in the factory, but the real test is a decade of hard work in a muddy, unforgiving field. How can you be sure that a new batch of rims will perform as well as the last one?
Rigorous testing protocols simulate real-world forces to validate a rim's design and manufacturing quality. Tests for radial fatigue, cornering fatigue, and impact resistance6 are essential to confirm that the rim can withstand extreme agricultural environments without failing.
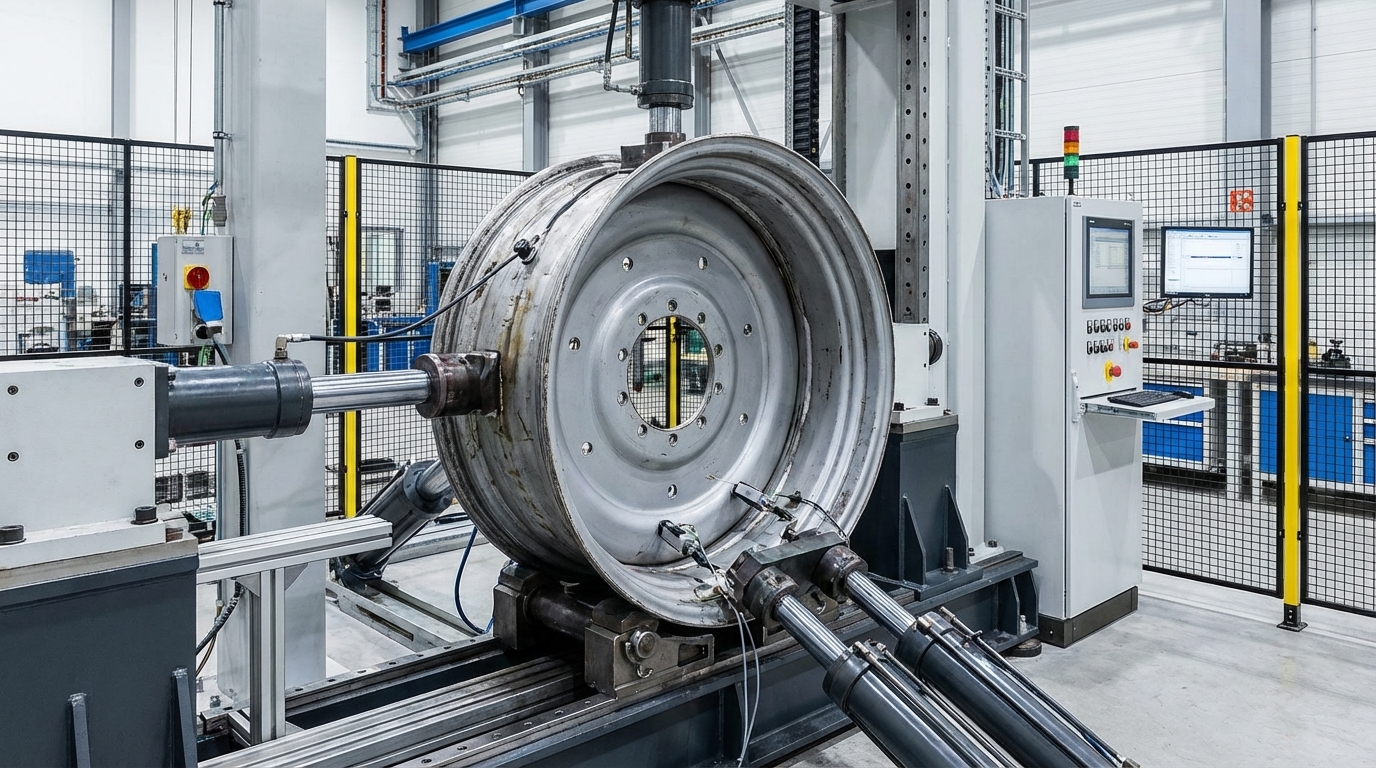

As an OEM, you can't afford to use your customers as your test lab. That's why a supplier's testing capability7 is non-negotiable. A spec sheet is just a promise; a test report is proof. We subject our rims to a battery of tests that simulate the worst conditions a tractor will ever face. The radial fatigue test simulates the stress of carrying a heavy load over millions of revolutions. The cornering fatigue test simulates the intense side forces placed on the rim disc and welds during tight turns. Finally, an impact test simulates hitting a rock or ditch at speed. Rims that pass these tests are proven to be reliable. When sourcing, you should always ask to see the supplier's testing data. A supplier who can't provide it is asking you to take a very expensive risk on their behalf.
Essential Tests for Agricultural Rims
| Test Type | What It Simulates | Why It's Critical |
|---|---|---|
| Radial Fatigue Test | The vertical load of the tractor and implement over millions of cycles. | Ensures the rim won't crack under constant weight and rolling pressure. |
| Cornering Fatigue Test | The intense lateral forces on the wheel during turns. | Validates the strength of the weld joint between the disc and the rim. |
| Impact Test | Hitting a large rock, pothole, or other field obstacles. | Confirms the rim can withstand sudden, sharp impacts without bending or breaking. |
Conclusion
For OEMs, sourcing agricultural steel rims is an engineering decision8, not a simple purchase. Partnering with a technically proficient supplier ensures reliability, protects your brand, and delivers a safer, more durable tractor to your customers.
Explore how high-strength steel enhances durability and performance in agricultural rims. ↩
Learn how precision in manufacturing can prevent failures and ensure safety in agricultural rims. ↩
Understand the impact of metal fatigue on the performance and safety of agricultural rims. ↩
Learn about the importance of proper welding techniques to prevent rim failures. ↩
Find out how automated welding enhances the quality and strength of agricultural rims. ↩
Learn how impact resistance is crucial for the durability of rims in challenging environments. ↩
Understand the significance of testing capabilities in selecting a reliable rim supplier. ↩
Understand the engineering considerations that make rim sourcing critical for OEMs. ↩


