You've built your business on a strong credit history1 to secure financing. Yet, you're finding that lenders are becoming more cautious, and the old rules for assessing risk no longer seem to guarantee access to capital.
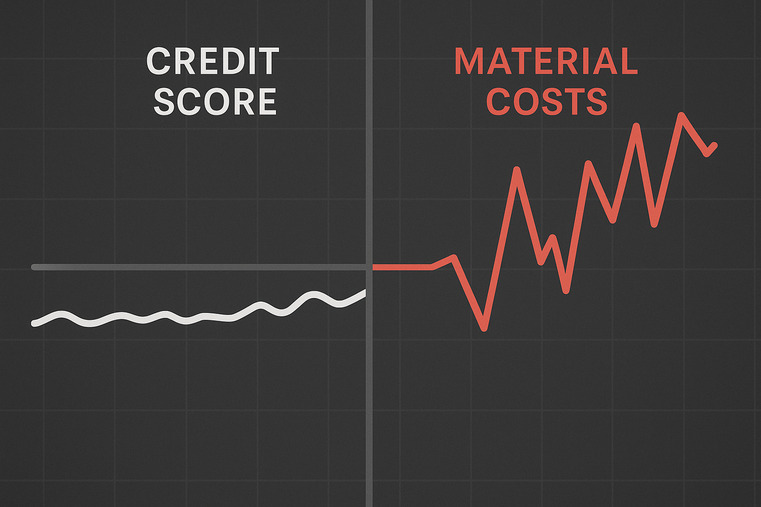
Because the primary repayment risk has shifted from buyer default to raw material volatility2. A sudden spike in the cost of rubber, steel, or carbon black can destroy the profit margin3 needed to repay a loan, making cost fluctuation4 the most critical financial risk variable.
I remember talking to a finance director for a large equipment distributor a while back. They had a perfect payment history and a top-tier credit rating. They went to their bank for a standard credit line to finance a large tire purchase. To their shock, the bank was hesitant. The bank wasn't worried about the distributor's ability to sell the tires or their customers' ability to pay. The bank's new question was, "What if the cost of rubber doubles between the time you place the order and the time you sell the inventory?" The entire financial equation had changed. The risk was no longer in the sales office; it was in the chemical makeup of the product itself.
Why is Material Risk Now a Bigger Threat Than Buyer Default?
You've always focused your financial risk analysis5 on your customer's creditworthiness. But even with reliable buyers, you feel a growing sense of financial uncertainty in your supply chain that you can't quite pinpoint.
Because a buyer's willingness to pay is useless if the transaction becomes unprofitable before payment is due. A sudden 30% spike in steel or rubber costs can eliminate your margin, turning a good sale into a financial loss.

For generations, the main question in trade finance was simple: "Will the buyer pay their bill?" We built entire systems of credit ratings and background checks to answer that question. But in today's market, that question is secondary. The new, more urgent question is: "Will the cost of producing the goods remain stable enough for there to be a profit to pay the bill with?" In a volatile supply chain6, your customer's perfect credit rating doesn't protect you if the cost of goods skyrockets. This material exposure is a risk that traditional credit models completely ignore. It's a hidden variable that has become the primary driver of financial instability for importers and distributors.
The Shift in Financial Risk Assessment
| Risk Factor | Old Model Focus | New Model Reality |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Variable | Buyer's credit score | Supplier's cost structure volatility |
| Key Question | Will the buyer default? | Will material costs spike? |
| Source of Risk | Customer's financial health | Global commodity markets |
| Mitigation Strategy | Credit checks, payment terms | Supplier engineering, cost stability |
Will Your Supplier's Material Exposure Affect Your Financing?
You assume that when a bank assesses your business, they only look at your balance sheet and sales history. You never considered that your supplier's business practices could directly impact your access to capital.
Yes, absolutely. Banks and financing platforms7 are beginning to assess suppliers based on their material-exposure risk, not just their financials. A supplier heavily dependent on volatile materials is now seen as a higher-risk partner, which increases the perceived risk of financing you.

Think of it from a lender's perspective. If they provide you with a credit line to buy tires, they are betting on your ability to sell those tires at a profit and pay them back. If your supplier's costs are unpredictable, then your profit margin3 is unpredictable. And if your profit is unpredictable, your ability to repay becomes a gamble. Smart financiers know this. They are starting to ask tougher questions. They want to know about your supplier's material sourcing strategy. They want to know if your costs are hedged or if you are exposed. A supplier with a stable cost structure makes you a safer bet. In this new era, your supplier's ability to control their material costs is becoming just as important as your own credit score.
How Does Cost Predictability Become a Financial Advantage?
You see cost stability as an operational benefit, helping with budgeting and pricing. You haven't yet connected how this stability could translate into a concrete financial advantage and cheaper funding for your business.
Because cost predictability8 dramatically reduces the risk for lenders. A business with a stable, predictable cost structure is a more reliable and lower-risk borrower. This lower risk profile translates directly into better financing terms and cheaper access to capital.

The future of supply chain finance will reward stability. The new key performance indicator for financial health is shifting from just looking at debt ratios to measuring "volatility immunity." Imagine two companies going for a loan. Company A uses a supplier with wildly fluctuating prices. Company B uses a supplier that guarantees cost stability through advanced material engineering and sourcing. For a bank, Company B is a much safer investment. They can accurately forecast Company B's margins and repayment ability. As a result, Company B will be offered more capital at a lower interest rate. This isn't just theory; it's the new reality of financial leverage9. Choosing a supplier with a stable cost structure is one of the most powerful financial decisions you can make.
Conclusion
The rules of finance are changing. Lenders now see that the greatest risk is not credit default, but material cost volatility. Partnering with a stable supplier10 is your best financial defense.
Explore how a strong credit history can influence your access to capital and financing options. ↩
Understanding material volatility is crucial for managing financial risks in supply chains. ↩
Learn about profit margins and their critical role in business profitability. ↩
Discover how cost fluctuations can affect profit margins and financial stability. ↩
Learn about financial risk analysis and its importance in today's volatile market. ↩
Explore the challenges posed by a volatile supply chain on business operations. ↩
Learn about financing platforms and their role in modern business financing. ↩
Understand how cost predictability can lead to better financing terms. ↩
Explore the concept of financial leverage and its impact on business growth. ↩
Choosing a stable supplier can significantly reduce financial risks. ↩


